This post by Laura Golakeh, a 2015 summer intern at the Wellesley Centers for Women, was originally published in The Analyst, a Liberian newspaper. It is posted here with permission.
 On March 11, 2021, the House of Representatives passed a bill seeking to “create a special education scheme to support deserving students attending public tertiary institutions across Liberia. The Bill is titled “An Act to Create a Special Education Fund to Support and Sustain the Tuition Free Scheme for the University of Liberia, All Public Universities and Colleges’ Program and the Free WASSCE fess for Ninth and Twelfth Graders in Liberia, or the Weah Education Fund (WEF) for short. The bill when enacted into law, will make all public colleges and universities “tuition-free”. The passage of this bill by the Lower House has been met by mixed reactions across the country: young, old, educated, not educated, stakeholders, parents, teachers among others, have all voiced their opinions about this bill. While some are celebrating this purported huge milestone in the education sector, others are still skeptical that this bill may only increase access but not address the structural challenges within the sector. I join forces with the latter, and in this article, I discuss the quality and access concept in our education sector and why quality is important than access. I recommend urgent action to improve quality for learners in K-12.
On March 11, 2021, the House of Representatives passed a bill seeking to “create a special education scheme to support deserving students attending public tertiary institutions across Liberia. The Bill is titled “An Act to Create a Special Education Fund to Support and Sustain the Tuition Free Scheme for the University of Liberia, All Public Universities and Colleges’ Program and the Free WASSCE fess for Ninth and Twelfth Graders in Liberia, or the Weah Education Fund (WEF) for short. The bill when enacted into law, will make all public colleges and universities “tuition-free”. The passage of this bill by the Lower House has been met by mixed reactions across the country: young, old, educated, not educated, stakeholders, parents, teachers among others, have all voiced their opinions about this bill. While some are celebrating this purported huge milestone in the education sector, others are still skeptical that this bill may only increase access but not address the structural challenges within the sector. I join forces with the latter, and in this article, I discuss the quality and access concept in our education sector and why quality is important than access. I recommend urgent action to improve quality for learners in K-12.
While this may sound like a broken record, an overview of our context is key in addressing the pertinent issues in my article. Liberia is still rebuilding its damaged education system after more than 14 years of crisis. Additionally, structural inequalities and the recent Ebola crisis in 2015, have contributed to challenges facing the education sector. While some gains have been made, Liberia is still behind many sub-Saharan countries in most education statistics. Poor learning outcomes, overage enrollment, unskilled and unqualified teachers, poor infrastructure are among some of the many challenges facing the sector. There are no national school quality standards and no proper monitoring mechanism at the county and district level. In 2013, all 25,000 candidates seeking admission at the University of Liberia, Liberia’s oldest degree granting institution failed the entrance exam. According to an official, the candidates lacked “enthusiasm and a grasp of basic English”. To put that into perspective, 25,000 individuals who went through K-12 lacked basic English skills needed to thrive in college. I put it that, quality is the issue, not access. A closer look at the following stats may help us understand this more clearly. It is no secret that Liberia has made progress in providing access to education, but has made limited progress in retaining learners. A World Bank report in 2016 showed that, of children who enroll in primary school in the country, 69 percent ‘survive’ to grade 6 and 59 percent ‘survive’ to grade 9. On the other hand, in the Education Quality and Access in Liberia (EQUAL) study, the mean score for Grade 3 oral reading fluency was 19.9 correct words per minute, compared to a mean score of 25 correct words per minute on the EGRAPlus assessment, and an average of 18.9 correct words per minute for Grade 3 students assessed by the Liberia Teacher Training Program (LTTP) II study. International benchmarks associated with literacy and comprehension are set at an oral reading fluency of between 45–65 correct words per minute. Again, the issue is quality and not access. It is not enough for a learner to have a seat in the classroom, the emphasis for policymakers is to guarantee that learner has quality education while they are sitting in that seat. The emphasis is to fix our broken system and ensure adequate funding for our schools. The emphasis is to overhaul our K-12 system and ensure our learners are graduating with relevant skills to succeed in their personal and professional endeavors. As one of my mentors and former boss said in a recent post on social media, we “cannot fix the roof while the foundation is collapsing”. This is a complete error in judgment. A careful review of the sector has brought me to the conclusion that focusing on quality in the system especially, K12 should be a key priority. Policymakers should also be cognizant of the following issues:
Teacher Quality and Societal Perception of Teachers: Goal 4 of the United Nations Sustainability Goals aims to “ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all”. Teachers therefore are needed to play a key role in achieving this goal by 2030. According to a World Bank report, about 62 percent of Liberian public school teachers are not qualified. Additionally, teachers especially public-school teachers are underpaid compared to other professions in the country. The “salary of teachers in Liberia range between US$140 to US$500 per month depending on their level of education. The lowest paid teachers, certificate holders, earn between US$100-US$ 140 while B certificate holders’ pocket US$ 180-US$ 200”. According to a study by the Center for Global Development conducted in 15 African countries, “teachers are paid either a lower or comparable monthly salary to other wage workers with similar educational background in three-quarters of African countries”. These issues make it difficult for the system to attract qualified teachers, hence the influx of unqualified teachers. According to an IREX report, research conducted to study perceptions of the teaching profession in Liberia showed that the profession is viewed by many as low compared to other professions in the country. It is true that a greater part of a teacher’s experience is based on how society views them and the profession in general. Countries like Singapore have the best education system because reverence for its teachers is well documented.
Bottomline, increase teacher’s compensation, provide professional development opportunities, ensure teachers are monitored and evaluated and engage in an advocacy and outreach campaign to change societal perceptions of the teaching profession. It is widely known that the social status of the teaching profession impacts recruitment and retention of effective teachers. Recent findings from the Global Teacher Index 2018 study suggests that there is a correlation between teacher status and student learning outcomes and that increasing teacher status can directly improve the pupil performance of a country’s students.
Reform Student Assessments: Education leaders need to promote a comprehensive and rigorous assessment systems that contribute to quality education. Student assessment reform is also a powerful stimulus for quality improvement in higher education and its reform goes well beyond the domain of assignments and examinations. Ensure classroom and large scale system level assessments are put in place to not only assess learning in the classroom but also continuous evaluation of the education system. Particular emphasis should be made to encourage teachers to design formative assessments that reflect students’ learning outcomes and that track individual students’ growth, rather than focusing on comparing students with one another. Teachers should be taught the necessary skills and expertise to carry out these assessments. A reform assessment module will serve to diagnose student learning issues, provide feedback to students on their learning, inform teaching, communicate with parents about their child’s learning, and meet school-level requirements on assessing student achievement. The goal is to graduate from traditional assessment to 21st century assessment.
Bottomline, ensure an enabling environment, system alignment and improve assessment quality.
21st Century/Competency Infused Curriculum: I wrote in a previous article, that a competency infused curriculum for education is essential for all learners in Liberia. Curriculum and quality works together. Our curriculum needs to be reformed to reflect our learners developing cognitive skills, practical skills, attitudes, emotions, values and ethics and motivation related to cooperation for learners. A quality education is one that prepares learners to be global citizens. The World Economic Forum defines global citizenship skills as those that focuses on building awareness about the wider world, sustainability and playing an active role in the global community.
Bottomline, a competency infused curriculum will lead to better learning outcomes for learners and better prepare them to thrive in the 21st century.
Gender Nudge: Gender awareness drives quality. In Liberia, as well as our education system, patriachal tendencies have led to a greater disadvantage for female and other vulnerable learners in classrooms. Poverty, disability, early marriage and pregnancy, gender-based violence, cultural ideals about the status and role of women in our society have helped build obstacles for female learners. Inorder for Liberia to ensure quality education for its citizenry, these gender related issues need to be addressed adequately.It is without any doubt that education policies and programs are bound to fail if gender is not mainstreamed in its designs and implementation.For example, a policy that wants to ensure that girls and women thrive in educational institutions should take into account that institutions do not work without interacting with and getting influenced by societal or cultural factors such as family, state, media and society. As a result, educational institutions are forced to perpetuate the stereotypes held against women in society. Such influences can stop women and girls from realizing their potential in academia as they are forced to encounter issues of discrimination, sexual harassment, dominancy of males among others.
Bottomline, mainstreaming gender in education policies and programs as a prerequisite for quality education.
Lastly, the Liberian Government needs to invest resources in the sector. Lawmakers should work with the Ministry of Education and other stakeholders to allocate more budget support for the sector. Liberia education spending for 2018 was 8.06% of its GDP, a 0.2% decline from 2017. Recently, civil society organizations in Liberia protested over an 8 percent decrease of the education budget from 570 million in 2018/2019 to 525 million in 2019/2020 national budget.
The education system is in serious need of a “fix” not a temporary political solution. I choose quality over access.
Laura Golakeh is a gender and education expert. She holds a Master of Arts degree in Gender and Peacebuilding and is currently a student at Harvard University pursuing a Master’s in International Education Policy. During the summer of 2015, Laura was an intern at the Wellesley Centers for Women.



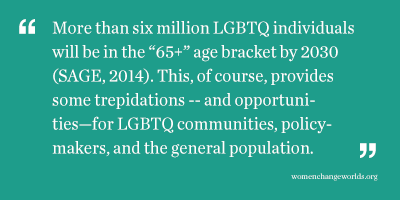 In the last couple of years, more research has surfaced regarding LGBTQ elderly people, which provides a sobering look at their attitudes and thoughts about aging. The first and obvious concern is aging in a society and community that places a high value on youth, leaving the elderly feeling useless and insignificant (Fox, 2007). This is both within the LGBTQ communities and in the general population. Ageism is pervasive in the U.S.
In the last couple of years, more research has surfaced regarding LGBTQ elderly people, which provides a sobering look at their attitudes and thoughts about aging. The first and obvious concern is aging in a society and community that places a high value on youth, leaving the elderly feeling useless and insignificant (Fox, 2007). This is both within the LGBTQ communities and in the general population. Ageism is pervasive in the U.S.

 s a precursor to teen dating violence. Schools—where most young people meet, hang out, and develop patterns of social interactions—may be training grounds for domestic violence because behaviors conducted in public may provide license to proceed in private.
s a precursor to teen dating violence. Schools—where most young people meet, hang out, and develop patterns of social interactions—may be training grounds for domestic violence because behaviors conducted in public may provide license to proceed in private.
 Utilizing such “rape myths” like the need for well-lit streets and women’s ability to walk safely perfectly illustrates Haugen’s limited understanding of sexual violence:
Utilizing such “rape myths” like the need for well-lit streets and women’s ability to walk safely perfectly illustrates Haugen’s limited understanding of sexual violence: 
 Social Justice Dialogue: Eradicating Poverty
Social Justice Dialogue: Eradicating Poverty
 The inadequacy of full-time, year-round minimum wage earnings to support a family. In 2009, single mothers earning the hourly minimum wage of $7.25 earned just over $15,000--well below the poverty level of $17,285 for a family of three. These earnings are far below the median U.S. family income (almost $50,000) and the median earnings of dual earning households (over $78,000).
The inadequacy of full-time, year-round minimum wage earnings to support a family. In 2009, single mothers earning the hourly minimum wage of $7.25 earned just over $15,000--well below the poverty level of $17,285 for a family of three. These earnings are far below the median U.S. family income (almost $50,000) and the median earnings of dual earning households (over $78,000).
 During the flight home, as I reviewed the day’s
During the flight home, as I reviewed the day’s 